Homophones and Homonyms in English
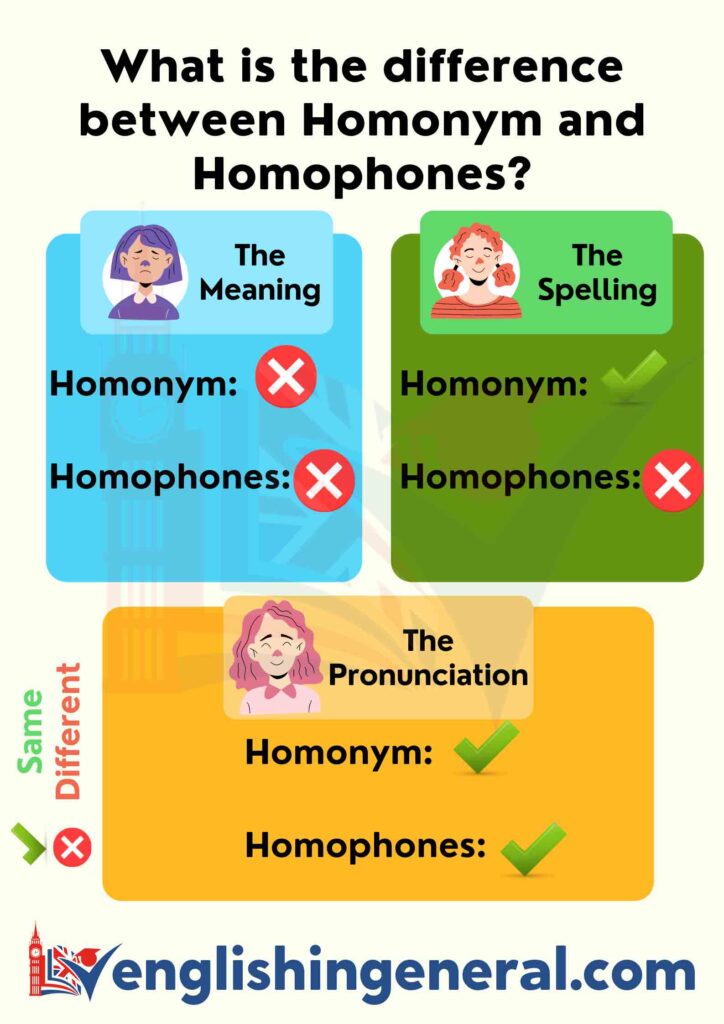
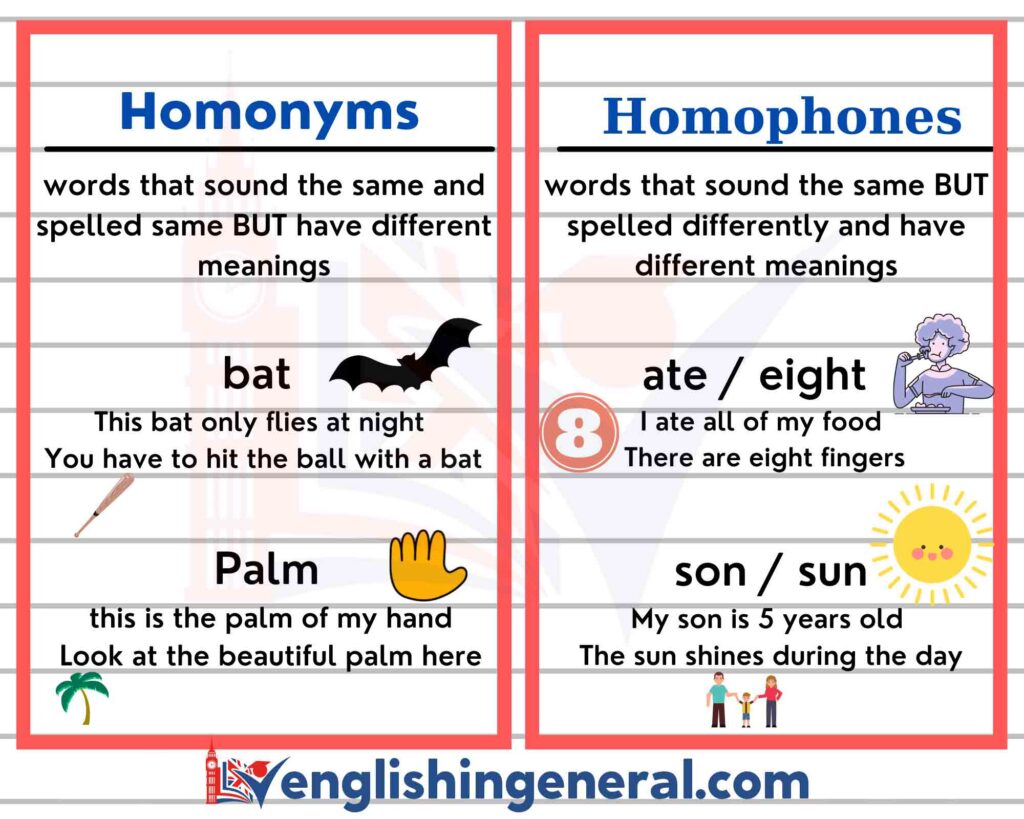
Homophones and homonyms are two linguistic terms related to the spellings and pronunciation of words. The main difference between homophones and homonyms is that homophones are words that share the same pronunciation but have different meanings whereas homonyms are words that have the same spelling or pronunciation but different meanings and origins.
What is Homophones?
The term homophone comes from the Greek “homo” and “semantic” sounds with the same meaning. A homophone is a word that sounds the same as another word but has a different meaning. The spelling of words may not differ in some cases. For example, the two words pear (fruit) and pair (set of two things) have no pronunciation difference. Among some other examples of homophones;
- Cereal (Grain used for food), serial (taking place in series)
- Flour (Ingredient), flower (plant)
- Meat (Food from the flesh of an animal), meet (Arrange or happen to cross paths with somebody)
What is Homonyms?
The term Homonyms is the name meaning “homo” and “onym” in Greek, which carry the same meaning. A homonym refers to two or more words that have the same spelling or pronunciation but different meanings and origins such as Address (a place) – Address (try to solve a problem). Among some other examples of Homonyms;
Band – Band
- The band was playing old Beatles songs.
- She always ties her hair back in a band.
- Many insects are banded black and yellow.
Bat – Bat
- I am afraid of bats.
- It’s his first time at bat in the major leagues.